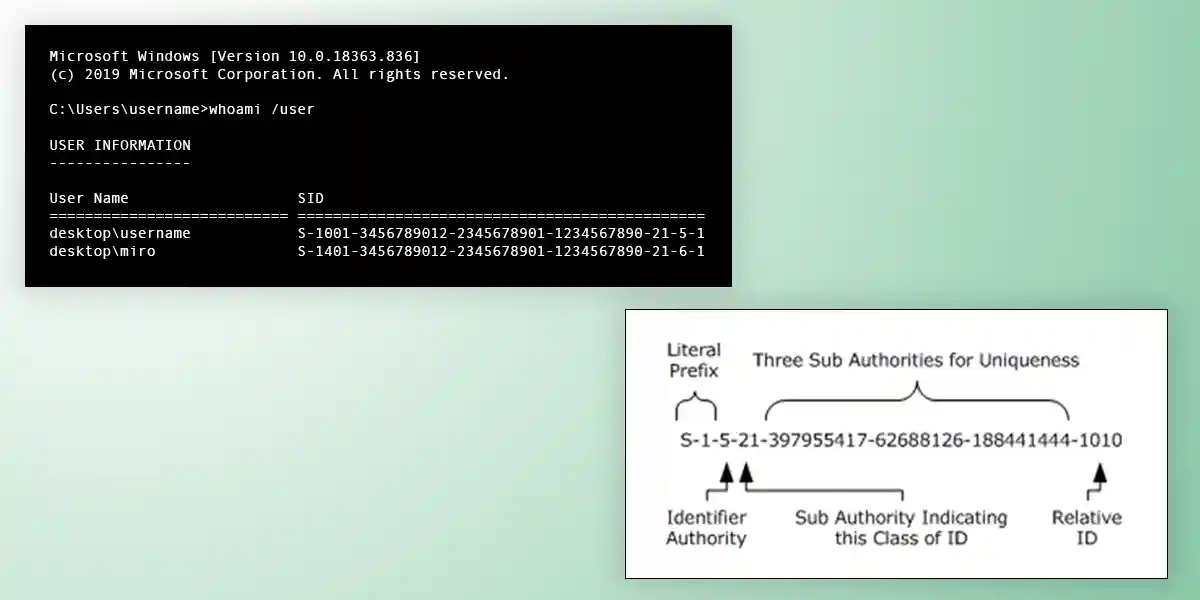
A Security Identifier (SID) is a unique identifier widely used in Microsoft’s
systems, such as identifying users within Windows or within an Active Directory.
The SID, a binary value of variable length, can also be represented as a string.
This conversion is facilitated by the function
ConvertSidToStringSid,
provided by the Advapi32.dll library, exclusive to Windows.
Therefore, to perform this conversion, one can either use Advapi32.dll
(Windows only) or rewrite the conversion algorithm. Having this conversion
implemented in a specific language, like Java, makes it universally usable.
After extensive research, I found that most available implementations were
incorrect, despite generally working. Hence, I decided to create my own Java
implementation, rigorously tested for accuracy.
A string SID follows this format:
S-1-IdentifierAuthority-SubAuthority1-SubAuthority2-...-SubAuthoritynThis syntax is formally defined using ABNF as follows:
SID= "S-1-" IdentifierAuthority 1*SubAuthority
IdentifierAuthority= IdentifierAuthorityDec / IdentifierAuthorityHex
; If the identifier authority is < 2^32, the
; identifier authority is represented as a decimal
; number
; If the identifier authority is >= 2^32,
; the identifier authority is represented in
; hexadecimal
IdentifierAuthorityDec = 1*10DIGIT
; IdentifierAuthorityDec, top level authority of a
; security identifier is represented as a decimal number
IdentifierAuthorityHex = "0x" 12HEXDIG
; IdentifierAuthorityHex, the top-level authority of a
; security identifier is represented as a hexadecimal number
SubAuthority= "-" 1*10DIGIT
; Sub-Authority is always represented as a decimal number
; No leading "0" characters are allowed when IdentifierAuthority
; or SubAuthority is represented as a decimal number
; All hexadecimal digits must be output in string format,
; pre-pended by "0x"Each field corresponds to a specific byte group in the binary SID, as officially detailed.
The final Java algorithm I implemented is as follows:
public static String convertSidToStringSid(byte[] sid) {
int offset, size;
// sid[0] is the Revision, we allow only version 1, because it's the
// only that exists right now.
if (sid[0] != 1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("SID revision must be 1");
StringBuilder stringSidBuilder = new StringBuilder("S-1-");
// The next byte specifies the numbers of sub authorities (number of
// dashes minus two)
int subAuthorityCount = sid[1] & 0xFF;
// IdentifierAuthority (6 bytes starting from the second) (big endian)
long identifierAuthority = 0;
offset = 2;
size = 6;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
identifierAuthority |= (long) (sid[offset + i] & 0xFF) << (8 * (size - 1 - i));
// The & 0xFF is necessary because byte is signed in Java
}
if (identifierAuthority < Math.pow(2, 32)) {
stringSidBuilder.append(Long.toString(identifierAuthority));
} else {
stringSidBuilder.append("0x").append(
Long.toHexString(identifierAuthority).toUpperCase());
}
// Iterate all the SubAuthority (little-endian)
offset = 8;
size = 4; // 32-bits (4 bytes) for each SubAuthority
for (int i = 0; i < subAuthorityCount; i++, offset += size) {
long subAuthority = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
subAuthority |= (long) (sid[offset + j] & 0xFF) << (8 * j);
// The & 0xFF is necessary because byte is signed in Java
}
stringSidBuilder.append("-").append(subAuthority);
}
return stringSidBuilder.toString();
}This algorithm was extensively tested by generating numerous SIDs and comparing
the results with those from the original Advapi32.dll conversion. For
instance, the following test function was used:
private static void generateCombinations(byte[] sid, int offset) throws Exception {
String convertedSid, convertedSid2;
if (offset >= sid.length) {
convertedSid = Advapi32Util.convertSidToStringSid(new PSID(sid));
convertedSid2 = convertSidToStringSid(sid);
if (!convertedSid.equals(convertedSid2)) {
throw new Exception("Conversion Error: "
+ convertedSid2 + " instead of " + convertedSid);
}
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= 255; i += 255/3) {
sid[offset] = (byte)(i & 0xFF);
generateCombinations(sid, offset+1);
}
}You can download the complete code along with tests from the following link: https://gist.github.com/miromannino/04be6a64ea0b5f4d4254bb321e09d628